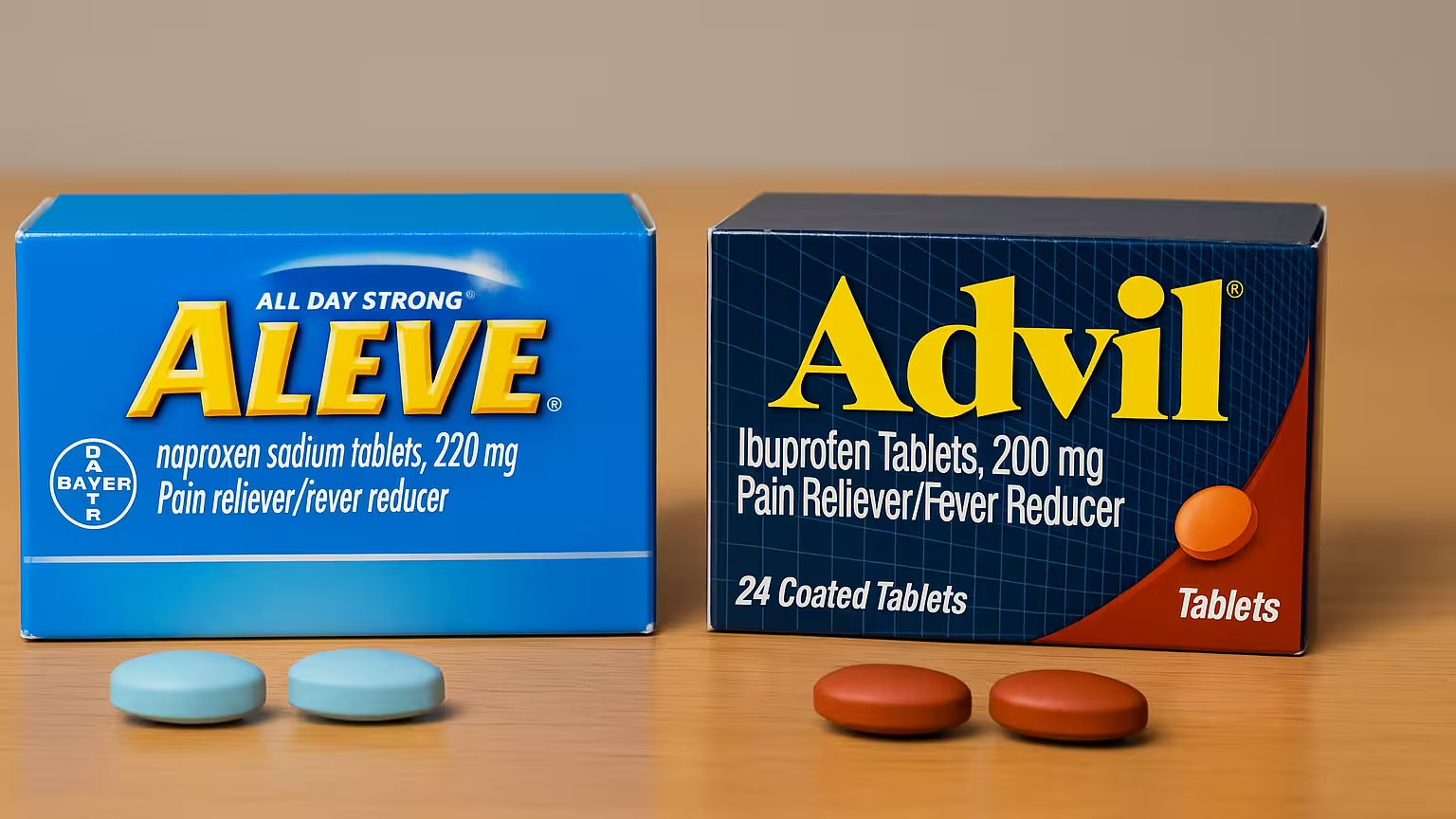
When you’re dealing with pain—whether it’s from a headache, backache, arthritis, or menstrual cramps—two common names likely come to mind: Aleve and Advil. These over-the-counter (OTC) medications are among the most widely used in the U.S. But knowing which one is better for your specific needs can help you feel better, faster—and stay safer.
In this guide, we’ll break down how Aleve and Advil work, their key differences, potential side effects, and how to use them safely. Let’s make pain relief simple and smarter.
Table of contents
Quick Snapshot
| Feature | Aleve | Advil |
|---|---|---|
| Active Ingredient | Naproxen Sodium | Ibuprofen |
| Onset of Action | 30–60 minutes | 20–30 minutes |
| Duration | 8–12 hours | 4–6 hours |
| Best For | Chronic pain, inflammation | Acute pain, fever |
| OTC Dose (Adults) | 220 mg every 8–12 hrs | 200–400 mg every 4–6 hrs |
| Max Daily Dose | 660 mg | 1200 mg |
| Common Brands | Aleve, Naprosyn | Advil, Motrin |
Aleve and Advil are both NSAIDs, but their unique characteristics make them more suitable for different situations. Understanding this can help you make more informed choices.
How They Work
Both Aleve (naproxen) and Advil (ibuprofen) work by reducing substances in the body that cause inflammation and pain. They are classified as Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs).
NSAIDs block two enzymes called COX-1 and COX-2, which are involved in the production of prostaglandins. These are chemicals that promote inflammation, pain, and fever. By reducing prostaglandins, both drugs help relieve discomfort.
- COX-1 also protects the stomach lining and supports kidney function.
- COX-2 is more involved in the inflammation process.
Because both drugs affect COX-1 and COX-2, they can reduce pain but may also cause side effects, especially in the stomach or kidneys.
Key Differences
1. Duration of Action
- Aleve is long-lasting, typically effective for 8 to 12 hours.
- Advil is shorter-acting and generally lasts 4 to 6 hours.
If you want a medication that provides all-day relief with fewer doses, Aleve may be more convenient. Advil, on the other hand, offers more control with shorter intervals between doses.
2. Dosing Frequency
- Aleve: 1 tablet every 8–12 hours (max 2 in 24 hours).
- Advil: 1–2 tablets every 4–6 hours (max 6 in 24 hours).
Advil is preferred by those who may need to take medication for pain only at specific times (like before bed or during work hours), while Aleve works well for long-lasting coverage.
3. Use in Children
- Advil has pediatric versions and is often recommended for children.
- Aleve is typically not recommended for children under 12.
4. Formulations
Both Aleve and Advil are available in tablets, caplets, liquid gels, and even topical formulas. Advil has more variety in children’s formulations.
Effectiveness by Pain Type
Here’s how each medication tends to perform for common pain types:
| Pain Type | Recommended Option |
|---|---|
| Headache | Advil |
| Menstrual Cramps | Aleve |
| Muscle Pain | Advil |
| Chronic Arthritis | Aleve |
| Fever | Advil |
| Tendonitis | Aleve |
| Toothache | Advil |
| Sprain or Strain | Advil |
For acute pain, like sudden headaches or fevers, Advil’s faster onset can be more effective. For long-term inflammation, like arthritis or menstrual pain, Aleve’s longer duration helps avoid frequent dosing.
Side Effects and Precautions
Both medications are generally safe when used occasionally and as directed, but long-term or high-dose use increases risks.
Common Side Effects
- Stomach upset
- Heartburn
- Dizziness
- Headache
Serious Risks (especially with long-term use)
- Gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers
- Kidney damage or reduced kidney function
- Elevated blood pressure
- Heart attack or stroke risk, especially in people with heart disease
Who Should Be Cautious?
- Individuals with asthma, heart conditions, or kidney/liver issues
- Those taking blood thinners or other NSAIDs
- People with a history of stomach ulcers or bleeding disorders
Important:
Always take NSAIDs with food or milk, and consult a healthcare provider if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Can You Take Aleve and Advil Together?
No, you should not take Aleve and Advil at the same time.
Both are NSAIDs and work the same way. Taking them together increases your risk of:
- Stomach bleeding
- Kidney damage
- Overdose of anti-inflammatory compounds
If one isn’t working well for you, try switching (after the current dose has worn off), or consider using acetaminophen (Tylenol) as an alternative. It works differently and can sometimes be used in combination under medical supervision.
Which One Should You Choose?
Here’s a quick guide to help you choose based on your situation:
| Condition | Best Choice | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Headache | Advil | Faster onset, shorter duration |
| Menstrual Pain | Aleve | Long-lasting relief for recurring cramps |
| Fever | Advil | Reduces fever quickly |
| Arthritis | Aleve | Consistent inflammation control |
| Back Pain | Either | Depends on duration and personal response |
| Toothache | Advil | Quick pain relief |
| Tendonitis | Aleve | Works well for long-term inflammation |
| Short-term sprains | Advil | Flexible dosing, effective for acute pain |
Always remember that individual response can vary. Try both (not together) at different times and observe which one works better for your specific type of pain.
Tips for Safe Use
Here are best practices to ensure NSAIDs work effectively without causing harm:
- Follow the label. Don’t exceed the recommended dose.
- Use only when necessary. Avoid regular use unless instructed by a doctor.
- Take with food or milk. This helps reduce stomach side effects.
- Avoid alcohol. It increases the risk of stomach bleeding.
- Monitor for side effects. Stop use and seek help if you experience chest pain, difficulty breathing, black stools, or severe stomach pain.
- Talk to a doctor if you’re taking other medications, especially blood thinners, steroids, or diuretics.
The Bottom Line
Both Aleve and Advil are highly effective and widely trusted for treating pain and inflammation. They belong to the same class (NSAIDs) but differ in how long they last, how often you need to take them, and what types of pain they handle best.
- Use Advil for quick, short-term relief like headaches, fevers, or sprains.
- Use Aleve for longer-lasting relief from conditions like arthritis or menstrual cramps.
If you have ongoing pain, chronic inflammation, or are taking medications for other conditions, talk to your doctor to decide which NSAID is right for you. Making an informed decision will ensure you get effective relief while protecting your overall health.